- Messages
- 1,229
- Reaction score
- 740
- Points
- 123
thankyouYes, you can simplify it in that way.
Answer is B.
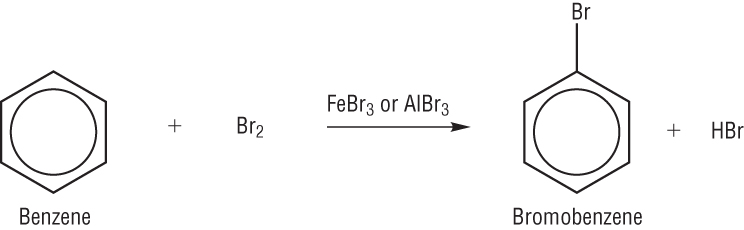
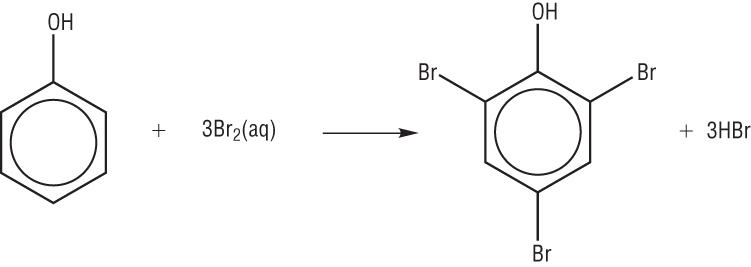
Q: whats the difference between methylbenzene and benzene reactions? For As level only
btw, see A and B give these products and none of them seems to be like the desired one to me