- Messages
- 84
- Reaction score
- 25
- Points
- 28
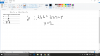
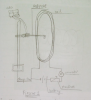
Please answer me the iv question.... I tried to solve it but the answer that i got is twice the actual answers. i got Vb = 866 but the answer is 433... and For Va the answer is 250 and i got 500... Please tell me what's missing....
Attachments
Last edited: