- Messages
- 140
- Reaction score
- 414
- Points
- 73
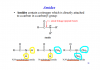
Can someone please tell me where 244 came from?
Yes, the bond energy of Cl2 is 242 in the 2016 specimen data booklet. The value must have been given as 244 in the data booklet of that particular year.So, I doubt that the marking scheme cites 244 kJ/mol since I think it would be 242 kJ/mol as per the data booklet and that is the enthalpy change of atomisation of Cl2 molecule which at have to take into consideration during the calculation.