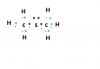
I think that is A Level stuff. This is for IGCSEi asked because both aldehyde and ketone undergoes nuclophilic addition
carboxylic acid also have cabonyl group why it does not undergoes nuclophilic addition by HCN
-
We need your support!
We are currently struggling to cover the operational costs of Xtremepapers, as a result we might have to shut this website down. Please donate if we have helped you and help make a difference in other students' lives!
Click here to Donate Now (View Announcement)
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Physics, Chemistry and Biology: Post your doubts here!
- Thread starter semsemhosam
- Start date
- Messages
- 9
- Reaction score
- 11
- Points
- 3
oh yes
it is in as level
it is in as level
- Messages
- 2
- Reaction score
- 2
- Points
- 1
Please help me what should i learn for my igcse atp exam for all sciences please hurry help meee
- Messages
- 2,144
- Reaction score
- 15,379
- Points
- 523
- Messages
- 2,144
- Reaction score
- 15,379
- Points
- 523
tHANKS BUT I DONT STUDY COMPUTER STUDIES ONLY ICT 0417
- Messages
- 110
- Reaction score
- 136
- Points
- 53
i know that this thread is for science subj. but this math formulae sheet would be helpful!!

http://www.wiziq.com/tutorial/194798-IGCSE-MATHEMATICS-FORMULA-BOOKLET-BY-BAAZ-MOHD-HILMY
http://www.wiziq.com/tutorial/194798-IGCSE-MATHEMATICS-FORMULA-BOOKLET-BY-BAAZ-MOHD-HILMY
- Messages
- 110
- Reaction score
- 136
- Points
- 53
- Messages
- 110
- Reaction score
- 136
- Points
- 53
somebody plz help!for hydrocarbons, when they are touched with a lighted splint do they give clear flame or yellow/blue flame?
 http://papers.xtremepapers.com/CIE/Cambridge IGCSE/Biology (0610)/0610_s03_ms_1+2+3+5+6.pdf
http://papers.xtremepapers.com/CIE/Cambridge IGCSE/Biology (0610)/0610_s03_ms_1+2+3+5+6.pdfPLz write a test for oxygen for biology!
y is there pyrogalo watevr that is in the mark scheme
plz reply
The simplest test for O2 is that it causes a glowing splint to burst in to flames. About the pyrohallot water, I don't know that testView attachment 40033http://papers.xtremepapers.com/CIE/Cambridge IGCSE/Biology (0610)/0610_s03_ms_1 2 3 5 6.pdf
PLz write a test for oxygen for biology!
y is there pyrogalo watevr that is in the mark scheme
plz reply
ya i know that, test but in mark schme its different!The simplest test for O2 is that it causes a glowing splint to burst in to flames. About the pyrohallot water, I don't know that test
- Messages
- 4
- Reaction score
- 3
- Points
- 13
Can someone please explain me the ionic equations...
Especially in this one

And this one please

Especially in this one

And this one please

- Messages
- 110
- Reaction score
- 136
- Points
- 53
Assalamu Alaykum , Here's some notes for you 
-You have to record the time taken for one complete oscillation by taking the time for more than one complete oscillation and divide it by their number , and this to reduce error and get more accurate value .
- check if the meter rule in an experiment is vertical by a set square .
- If something directly proportional it should have constant gradient , straight line and begins from the origin .
-To avoid parallax error , your eye should be perpendicular to the reading.
- As the temperature difference between water and room temperature increases , the drop in temperature also increases and vice versa .
-Distance measured between the object and the lens , and between the screen and the lens , must be taken from the center of the lens .
-you need to know the relation between the diameter and the resistance and the area and the resistance of the wire , For example , if diameter increased by 2 times , the resistance will be decreased 4 times , and if the area increased by 2 times , the resistance will be decreased two times .
- Centre of mass
Centre of mass is an imaginary point in a body (object) where the total mass of the
body canbe thought to be concentrated to make calculations easier
To find the centre of gravity on a flat object, use the following steps:
1. Get a flat object.
2. Get a stand and a plumb line (a string with a weight on it).
3. Punch 3 holes in your object.
4. Hang your object from the hole, and attach the plumb line to the same hole.
Draw a vertical line where the plumb line is.
5. Repeat step 4 for all the other holes. Where the lines meet is the centre of gravity.
(FIY the string should be able to swing freely, so should not touch the paper)
For stability the centre of mass must be over the centre of pressure.
DON'T FORGET THE UNITS ! .. It will cost you marks that u are in desperate need for it .
http://g2physics.wikispaces.com/file/view/EXAMINER TIPS FOR IGCSE PHYSICS 0625 (S04).pdf
<-- Examiner tips .
http://www.cambridgestudents.org.uk/subjectpages/physics/igscephysics/Learner Guide for IGCSE Physics 0625.pdf <--- Learner guide .
http://www.docseek.net/ktmhsm/notes-to-study-for-physics-paper-6.html <-- paper 6 notes .
http://hgphysics.files.wordpress.com/2012/11/tips-4-p6-exam.pdf .
http://www.xtremepapers.com/community/threads/atp-preparation.12572/ .
http://www.xtremepapers.com/communi...y-paper-2-2012-discussions.16598/#post-289636 .
https://www.xtremepapers.com/commun...ctical-notes-addendum-to-syllabus-424kb.5257/ .
http://www.xtremepapers.com/community/threads/amazing-notes-for-physics-paper-6.16788/ .
http://salman-olevelnotes.blogspot.ae/p/physics.html .
http://www.igcsephysicstutor.com/index/paper-6-doing-tables-and-graphs.html .
https://www.xtremepapers.com/commun...-tips-experiments-and-feqs.25526/#post-520779 .
https://www.xtremepapers.com/community/threads/physics-practical-videos-for-atp.22625/ .
https://www.xtremepapers.com/community/threads/physics-practical-tips.6306/ .
https://www.xtremepapers.com/community/threads/physics-general-tips.16304/#post-280944.
After studying those tips well , do few past papers ..
anw , That's some notes for now it will be always updated , if you have any notes and tips please post it here , don't ever hesitate . Let us make this post rich and worth reading
it will be always updated , if you have any notes and tips please post it here , don't ever hesitate . Let us make this post rich and worth reading 
May Allah give u all success in this world .. Good Luck in your studying , and A* in your exam

source: GorgeousEyes
-You have to record the time taken for one complete oscillation by taking the time for more than one complete oscillation and divide it by their number , and this to reduce error and get more accurate value .
- check if the meter rule in an experiment is vertical by a set square .
- If something directly proportional it should have constant gradient , straight line and begins from the origin .
-To avoid parallax error , your eye should be perpendicular to the reading.
- As the temperature difference between water and room temperature increases , the drop in temperature also increases and vice versa .
-Distance measured between the object and the lens , and between the screen and the lens , must be taken from the center of the lens .
-you need to know the relation between the diameter and the resistance and the area and the resistance of the wire , For example , if diameter increased by 2 times , the resistance will be decreased 4 times , and if the area increased by 2 times , the resistance will be decreased two times .
- Centre of mass
Centre of mass is an imaginary point in a body (object) where the total mass of the
body canbe thought to be concentrated to make calculations easier
To find the centre of gravity on a flat object, use the following steps:
1. Get a flat object.
2. Get a stand and a plumb line (a string with a weight on it).
3. Punch 3 holes in your object.
4. Hang your object from the hole, and attach the plumb line to the same hole.
Draw a vertical line where the plumb line is.
5. Repeat step 4 for all the other holes. Where the lines meet is the centre of gravity.
(FIY the string should be able to swing freely, so should not touch the paper)
For stability the centre of mass must be over the centre of pressure.
DON'T FORGET THE UNITS ! .. It will cost you marks that u are in desperate need for it .
http://g2physics.wikispaces.com/file/view/EXAMINER TIPS FOR IGCSE PHYSICS 0625 (S04).pdf
<-- Examiner tips .
http://www.cambridgestudents.org.uk/subjectpages/physics/igscephysics/Learner Guide for IGCSE Physics 0625.pdf <--- Learner guide .
http://www.docseek.net/ktmhsm/notes-to-study-for-physics-paper-6.html <-- paper 6 notes .
http://hgphysics.files.wordpress.com/2012/11/tips-4-p6-exam.pdf .
http://www.xtremepapers.com/community/threads/atp-preparation.12572/ .
http://www.xtremepapers.com/communi...y-paper-2-2012-discussions.16598/#post-289636 .
https://www.xtremepapers.com/commun...ctical-notes-addendum-to-syllabus-424kb.5257/ .
http://www.xtremepapers.com/community/threads/amazing-notes-for-physics-paper-6.16788/ .
http://salman-olevelnotes.blogspot.ae/p/physics.html .
http://www.igcsephysicstutor.com/index/paper-6-doing-tables-and-graphs.html .
https://www.xtremepapers.com/commun...-tips-experiments-and-feqs.25526/#post-520779 .
https://www.xtremepapers.com/community/threads/physics-practical-videos-for-atp.22625/ .
https://www.xtremepapers.com/community/threads/physics-practical-tips.6306/ .
https://www.xtremepapers.com/community/threads/physics-general-tips.16304/#post-280944.
After studying those tips well , do few past papers ..
anw , That's some notes for now
May Allah give u all success in this world .. Good Luck in your studying , and A* in your exam
source: GorgeousEyes
Last edited:
- Messages
- 110
- Reaction score
- 136
- Points
- 53
in physics p6 what is the arrangement of a set square either side of a cylinder/sphere to measure diameter??
Plz some help over here! and i would really appreciate if some one helped me with the doubts i posted earlier.
Plz some help over here! and i would really appreciate if some one helped me with the doubts i posted earlier.
Last edited:
- Messages
- 110
- Reaction score
- 136
- Points
- 53
Centre of mass experiment (with the lamina): How to minimize inaccuracy when marking the lines : you view the string directly in front of card.
Why angle i is NOT equale to angle r in ray experiment:
- thickness of pins
-thickness of mirror
-protractor is not precise
In an experiment to do with the cooling of water, there are certain things which must be kept the same:
- initial temp.
-thickness of test-tubes ( more heat lost when thinner etc.)
-vol. of water
-thickness of cotton wool
-depth of the thermometer in the water
-avoid droughts
Examples of insulators that you can wrap things with:
-bubble wrap
-fiberglass
Styrofoam is a good insulator , however you cannot wrap it around things as it breaks easily.
inaccuracy of ray box method: thickness of rays.
inaccuracy of pin method: pins not straight, or too close, or thickness of lines drawn.
Symbol for extension is 'x' or 'e'.
A ruler is called a 'rule'.
ALWAYS ROUND TO 3.SIG.FIGS.
To improve accuracy, put pins in the light ray experiment FURTHER APART to avoid parallax error. So, I I I is better than I I I (where I is the pins)
Precautions for circuit readings of I and V so that accurate:
For I specifically :
-limit current so that temp. doesn't increase
-use a tapping meter
For I and V: Switch off between readings.
θ this is the symbol for Celsius temp. (theta)
T this is the symbol for Kelvin temp.
In light ray experiment, lengths are in mm.
Fair test for pendelum experiments:
-length of pendelum
-shape of bob
-no. of swings
-amplitude
If a statement is 'directly proportional', the justification would always be , ''straight line that goes through the origin''.
If you're comparing the extensions of springs of different materials, certain things have to be the same:
-the cross-section of the springs
-the length of the springs
-no. of coils
-range of loads
-length of wire
How to reduce the heating effect of current:
-Add a variable resistor
-reduce current
-reduce voltage or power
-switch off between readings
Precautions for focal length experiments:
-do it in a darkened room
-clamp ruler to bench
-avoid parallax error when reading the lengths
-make sure that the obejct/lense/screen are all perpendicular to bench.
-and of course, repeats.
A question one came up and asked to draw a diagram of a load on a ruler on a pivot. Well, this meant that the ruler was unbalanced, and so this means that when you draw it, you must show that the ruler is tilted.
DON'T FORGET TO WRITE DOWN THE UNITS AFTER EACH ANSWER!!
An important precaution for spring experiments is to wait for the spring to stop moving and then record the length.
source: balloonsandhighlighters
Why angle i is NOT equale to angle r in ray experiment:
- thickness of pins
-thickness of mirror
-protractor is not precise
In an experiment to do with the cooling of water, there are certain things which must be kept the same:
- initial temp.
-thickness of test-tubes ( more heat lost when thinner etc.)
-vol. of water
-thickness of cotton wool
-depth of the thermometer in the water
-avoid droughts
Examples of insulators that you can wrap things with:
-bubble wrap
-fiberglass
Styrofoam is a good insulator , however you cannot wrap it around things as it breaks easily.
inaccuracy of ray box method: thickness of rays.
inaccuracy of pin method: pins not straight, or too close, or thickness of lines drawn.
Symbol for extension is 'x' or 'e'.
A ruler is called a 'rule'.
ALWAYS ROUND TO 3.SIG.FIGS.
To improve accuracy, put pins in the light ray experiment FURTHER APART to avoid parallax error. So, I I I is better than I I I (where I is the pins)
Precautions for circuit readings of I and V so that accurate:
For I specifically :
-limit current so that temp. doesn't increase
-use a tapping meter
For I and V: Switch off between readings.
θ this is the symbol for Celsius temp. (theta)
T this is the symbol for Kelvin temp.
In light ray experiment, lengths are in mm.
Fair test for pendelum experiments:
-length of pendelum
-shape of bob
-no. of swings
-amplitude
If a statement is 'directly proportional', the justification would always be , ''straight line that goes through the origin''.
If you're comparing the extensions of springs of different materials, certain things have to be the same:
-the cross-section of the springs
-the length of the springs
-no. of coils
-range of loads
-length of wire
How to reduce the heating effect of current:
-Add a variable resistor
-reduce current
-reduce voltage or power
-switch off between readings
Precautions for focal length experiments:
-do it in a darkened room
-clamp ruler to bench
-avoid parallax error when reading the lengths
-make sure that the obejct/lense/screen are all perpendicular to bench.
-and of course, repeats.
A question one came up and asked to draw a diagram of a load on a ruler on a pivot. Well, this meant that the ruler was unbalanced, and so this means that when you draw it, you must show that the ruler is tilted.
DON'T FORGET TO WRITE DOWN THE UNITS AFTER EACH ANSWER!!
An important precaution for spring experiments is to wait for the spring to stop moving and then record the length.
source: balloonsandhighlighters
Last edited:
- Messages
- 1,095
- Reaction score
- 899
- Points
- 123
how are fungi , viruses and bacteria adapted to their envoirnment ?
sme1 plz ans cnt find it in book
sme1 plz ans cnt find it in book
Viruses can rapidly multiply and are only destroyed by the immune system of a bodyhow are fungi , viruses and bacteria adapted to their envoirnment ?
sme1 plz ans cnt find it in book
Bacteria have a tail (flagellum) to aid in swimming. They rapidly reproduce, colonizing other areas. They can feed on decaying matter. Have a cell wall to protect themselves.
Fungi can reproduce by spores. Release enzymes in the surrounding to break down organic matter (digestion), and then absorb it into it. Have numerous glycogen granules in its cytoplasm. It also has a proper nucleus
- Messages
- 110
- Reaction score
- 136
- Points
- 53
viruses:how are fungi , viruses and bacteria adapted to their envoirnment ?
sme1 plz ans cnt find it in book
-have a central core of DNA or RNA surrounded by protien coat, they dont have nucleus, cell organelles or cell membrane
-they dont show characteristics of living organisms except reproduction
-can live outside host cell, but can only reproduce inside a living cell
-the cell may be destroyed during reproduction of viruses or the viruses may escape wrapping themselves in peices of host's
cell membraneas they do so . these activities give rise to symptoms of disease.
-viruses may be used as vectors in genetic engineering
-they are parasites and the smallest disease causing particles
-they are particles not cells
-can only be destroyed by body's immune system
Bacteria:
-has cellmembrane, cellwall and cytoplasm containing rhibosomes
-has a circular loop of DNA
-some move by means of flagella
-dont have nuclear envelope thus no true nucleus
-has small rings of DNA called plasmids in the cytoplasm
-bacteria may be: saprophytic(feediing on decaying matter), Parasitic(causing diseases in living org.) or autotrophic( able to manufacture
their food using energy from sun or inorganic compounds "though they dont have chloroplasts instead they have chlorophyll like pigments")
-some are aerobic, some are anaerobic and some are both
-Reproduce by binary fission
-killed by antibiotics
-have cells but without nucleus
-cause diseases, but have helpful roles in carbon cycle, nitrogen cycle, making food,in treatment of sewage and in making insulin
-often unicellular
-have cellwall made of murin
-most live in or on food. release enzymes which digest food and then absorb the liq. product of digestion back into the bacterial cell.
-most pathogenic bactreia produce poisonous waste products called toxins
Fungi:
-multicellular
-some are parasits mots are saprotrophs living on dead matter the hyphae secretes enzymes into organic material and digest the liq. products, these
products are then absorbed back into the hyphae and used to provide energy or for production of new cytoplasm or for hyphal walls
-many are not made up of threads but of microscopic threads called hyphae (network of hyphae is called mycelium)
-reproduce by releasing single celled spores
-the hyphae are lined up with cytoplasm ,in older hyphae there is a vacuole and cytoplasm containing organelles and lipid droplets
-there are no chloroplasts or granules of starch in cytoplasm
-the hyphal cell wall may contain cellulose or chitin or both
-have nuclei
-yeast are single celled fungi which reproduce by budding , they live in situations where sugar is likely to be available
-yeast cells contain many enzymes some which can break down sugar into CO2 and alcohol (fermentation, it is a form of anaerobic respiration but if
yeast are supplied with carbohydrates other than sugar they yeast need oxygen to convert carbohydrates to sugar first)
i compiled these notes from different books, so i hope it helped (pray for all of us to get straight A*)
- Messages
- 1,095
- Reaction score
- 899
- Points
- 123
Thnx they helped alotviruses:
-have a central core of DNA or RNA surrounded by protien coat, they dont have nucleus, cell organelles or cell membrane
-they dont show characteristics of living organisms except reproduction
-can live outside host cell, but can only reproduce inside a living cell
-the cell may be destroyed during reproduction of viruses or the viruses may escape wrapping themselves in peices of host's
cell membraneas they do so . these activities give rise to symptoms of disease.
-viruses may be used as vectors in genetic engineering
-they are parasites and the smallest disease causing particles
-they are particles not cells
-can only be destroyed by body's immune system
Bacteria:
-has cellmembrane, cellwall and cytoplasm containing rhibosomes
-has a circular loop of DNA
-some move by means of flagella
-dont have nuclear envelope thus no true nucleus
-has small rings of DNA called plasmids in the cytoplasm
-bacteria may be: saprophytic(feediing on decaying matter), Parasitic(causing diseases in living org.) or autotrophic( able to manufacture
their food using energy from sun or inorganic compounds "though they dont have chloroplasts instead they have chlorophyll like pigments")
-some are aerobic, some are anaerobic and some are both
-Reproduce by binary fission
-killed by antibiotics
-have cells but without nucleus
-cause diseases, but have helpful roles in carbon cycle, nitrogen cycle, making food,in treatment of sewage and in making insulin
-often unicellular
-have cellwall made of murin
-most live in or on food. release enzymes which digest food and then absorb the liq. product of digestion back into the bacterial cell.
-most pathogenic bactreia produce poisonous waste products called toxins
Fungi:
-multicellular
-some are parasits mots are saprotrophs living on dead matter the hyphae secretes enzymes into organic material and digest the liq. products, these
products are then absorbed back into the hyphae and used to provide energy or for production of new cytoplasm or for hyphal walls
-many are not made up of threads but of microscopic threads called hyphae (network of hyphae is called mycelium)
-reproduce by releasing single celled spores
-the hyphae are lined up with cytoplasm ,in older hyphae there is a vacuole and cytoplasm containing organelles and lipid droplets
-there are no chloroplasts or granules of starch in cytoplasm
-the hyphal cell wall may contain cellulose or chitin or both
-have nuclei
-yeast are single celled fungi which reproduce by budding , they live in situations where sugar is likely to be available
-yeast cells contain many enzymes some which can break down sugar into CO2 and alcohol (fermentation, it is a form of anaerobic respiration but if
yeast are supplied with carbohydrates other than sugar they yeast need oxygen to convert carbohydrates to sugar first)
i compiled these notes from different books, so i hope it helped (pray for all of us to get straight A*)