-
We need your support!
We are currently struggling to cover the operational costs of Xtremepapers, as a result we might have to shut this website down. Please donate if we have helped you and help make a difference in other students' lives!
Click here to Donate Now (View Announcement)
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Mathematics: Post your doubts here!
- Thread starter XPFMember
- Start date
- Messages
- 2,206
- Reaction score
- 2,824
- Points
- 273
solving left hand side,
open up the bracket which gives u... cos^2x+6sinxcosx+9sin^2x
use the identity sin2x=2sinxcosx
so u need to get 6sinxcosx so multilpy it by 3... 3sin2x=6cosxsinx
equation becomes cos^2x+3sin2x+9sin^2x
so simplifying it further cos^2x+3sin2x+9(1-cos^2x)
cos^2x+3sin2x+9-9cos^2x
-8cos^2x+9+3sin2x
if u look at 5-4cos2x....its basically the same as -8cos^2x+9 when u simplify it so replace it with that...
thus 5-4cos2x+3sin2x proven
u need to show them how u converted the 5-4cos2x into -8cos^2x+9
open up the bracket which gives u... cos^2x+6sinxcosx+9sin^2x
use the identity sin2x=2sinxcosx
so u need to get 6sinxcosx so multilpy it by 3... 3sin2x=6cosxsinx
equation becomes cos^2x+3sin2x+9sin^2x
so simplifying it further cos^2x+3sin2x+9(1-cos^2x)
cos^2x+3sin2x+9-9cos^2x
-8cos^2x+9+3sin2x
if u look at 5-4cos2x....its basically the same as -8cos^2x+9 when u simplify it so replace it with that...
thus 5-4cos2x+3sin2x proven
u need to show them how u converted the 5-4cos2x into -8cos^2x+9
- Messages
- 1,318
- Reaction score
- 1,374
- Points
- 173
- Messages
- 1,318
- Reaction score
- 1,374
- Points
- 173
- Messages
- 1,318
- Reaction score
- 1,374
- Points
- 173
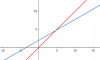
View attachment 59189
Can someone please show me how to do this ?
How do you find the least value of |z-w| ?
- Messages
- 1,318
- Reaction score
- 1,374
- Points
- 173
Least value is the distance D-CHow do you find the least value of |z-w| ?
so find AC by using sine rule
AC = 3root2/2
DC = AC - 1
Since the radius of circle is 1
So DC = (3root2/2)-1 = 1.12
Can you please show it in a diagram ?
- Messages
- 1,318
- Reaction score
- 1,374
- Points
- 173
I mean the argand diagram if you can please ?
- Messages
- 1,318
- Reaction score
- 1,374
- Points
- 173
That is the same as the argand diagram ... y corresponds to imaginary axis and x corresponds to real axisI mean the argand diagram if you can please ?
Can you please show how to obtain the answers using trigonometry on the diagram ?That is the same as the argand diagram ... y corresponds to imaginary axis and x corresponds to real axis
- Messages
- 1,318
- Reaction score
- 1,374
- Points
- 173
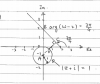
Can you please show how to obtain the answers using trigonometry on the diagram ?

Magnifying the triangle we can find the angles and use the sine rule
The argument of blue line is given in question as pi/6
red is y=x hence the argument is pi/4
Knowing these 2 angles you can find the other angles
We know the blue line cuts the imaginary axis at 2 (when we solved the equation above) so the length will be 2
Now apply the sine rule as x = [2/sin(pi/2)] * [sin(2pi/3)]
- Messages
- 140
- Reaction score
- 414
- Points
- 73
acosθ + bsinθ = rsin(θ+α) or rsin(θ-α) or rcos(θ+α) or rcos(θ-α)
How do I know when to use what? :O
How do I know when to use what? :O
- Messages
- 1,318
- Reaction score
- 1,374
- Points
- 173
Learn them:acosθ + bsinθ = rsin(θ+α) or rsin(θ-α) or rcos(θ+α) or rcos(θ-α)
How do I know when to use what? :O
acosθ + bsinθ = rcos(θ-α)
acosθ - bsinθ = rcos(θ+α)
asinθ + bcosθ = rsin(θ+α)
asinθ - bcosθ = rsin(θ-α)
When cos is first it's rcos and the signs in brackets are opposite to LHS
When sin is first it's rsin and the signs in brackets are same as LHS
- Messages
- 140
- Reaction score
- 414
- Points
- 73
I didn't know this ... damn, tysm!!!Learn them:
acosθ + bsinθ = rcos(θ-α)
acosθ - bsinθ = rcos(θ+α)
asinθ + bcosθ = rsin(θ+α)
asinθ - bcosθ = rsin(θ-α)
When cos is first it's rcos and the signs in brackets are opposite to LHS
When sin is first it's rsin and the signs in brackets are same as LHS